Nhân dịp đọc tin tức về việc FED nâng lãi suất, tối 16/12/2015, nhận thấy khái niệm cũ nhưng có lẽ đối với nhiều bạn, có thể lâu quá nên không nhớ, hoặc những anh/chị làm ngoài ngành sẽ lờ mờ không hiểu. Tôi xin note lại ở đây để mọi người cùng nắm.
Đường cong Phillips đại ý nói rằng lạm phát và thất nghiệp có mối quan hệ nghịch đảo. Các nhà điều hành chính sách có thể lợi dụng điểm này để điều hành nền kinh tế.
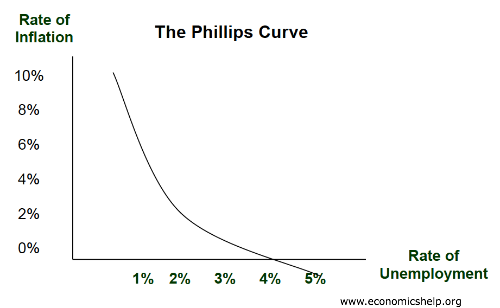
Ví dụ, nếu thất nghiệp đang cao và lạm phát đang thấp, nhà điều hành có thể kích thích tổng cầu, khi đó thất nghiệp sẽ giảm và tạo điều kiện cho lạm phát tăng trở lại.
Tuy vậy, hiện tượng đình lạm (stagflation) vào thập niên 1970 đã làm cho lý thuyết này lung lay, nền kinh tế khi đó xảy ra đồng thời cả hiện tượng thất nghiệp cao và lạm phát cao. Tuy vậy, trong hầu hết thời gian khác lạm phát và thất nghiệp thường có thể đánh đổi lẫn nhau.
Nguyên bản của đường cong Phillips là nghiên cứu mối quan hệ giữa tiền lương và tỷ lệ thất nghiệp, theo đó, tỷ lệ thất nghiệp thường cao khi tiền lương giảm và ngược lại. Sau đó, tác giả mới tìm được bằng chứng cho thấy giữa thất nghiệp và lạm phát có mối tương quan nghịch.
Vậy cơ chế đánh đổi giữa thất nghiệp và lạm phát như thế nào?
Việc tăng lên của tổng cầu từ AD lên AD2 làm cho tăng trưởng GDP tăng từ Y1 lên Y2, tăng trưởng kinh tế cao hơn giúp doanh nghiệp thuê mướn nhiều lao động hơn và thất nghiệp giảm.
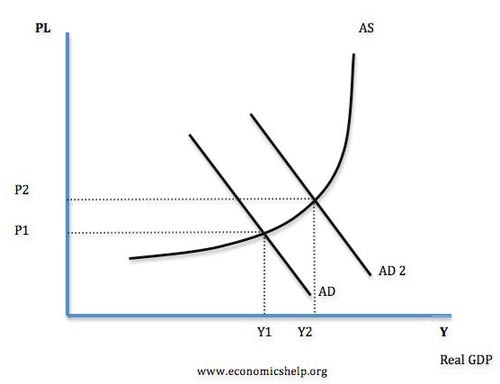
Tuy vậy, khi nền kinh tế càng gần đến công suất tối đa, thì áp lực lạm phát sẽ gia tăng. Với tỷ lệ thất nghiệp thấp hơn, nhân công có nhu cầu cao hơn nhờ tiền lương gia tăng và doanh nghiệp có thể gia tăng giá bán nhờ cầu tăng.
Mọi việc không đơn giản như vậy, vì sự thất bại của lý thuyết vào những năm 1970 mà quan điểm đường cong Phillips của những nhà kinh tế tiền tệ có chút khác biệt.
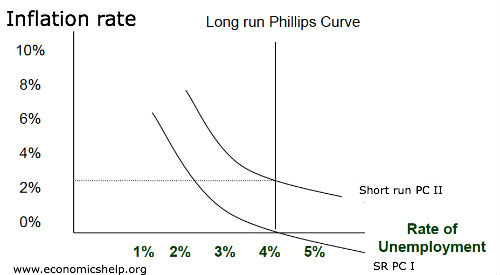
Họ cho rằng, khi tổng tổng cầu tăng lên, nhu cầu lao động giúp tiền lương danh nghĩa tăng lên. Khi người lao động thấy tiền lương danh nghĩa tăng lên họ sẽ làm nhiều giờ hơn để tìm kiếm thu nhập, nhưng sự thật không phải vậy, sự tăng lên của tiền lương kia là do lạm phát, nên dẫn đến kỳ vọng của người lao động sẽ thay đổi, họ giảm giờ làm trở lại và tỷ lệ thất nghiệp sẽ tăng lên như cũ.
Tóm lại
Nếu nền kinh tế đang vận hành dưới công suất tối đa, hầu hết nhà kinh tế học đều đồng ý lạm phát và thất nghiệp có thể đánh đổi nhau trong ngắn hạn, nhưng trong dài hạn thì phải xem lại.
Để thực chứng lý thuyết vào thực tế điều hành chính sách, các bạn có thể đọc bài “Why Fed may hike rates before seeing whites of inflation's eyes”
ANALYSIS By Jason Lange
10/28/2015, 3:31:27 AM
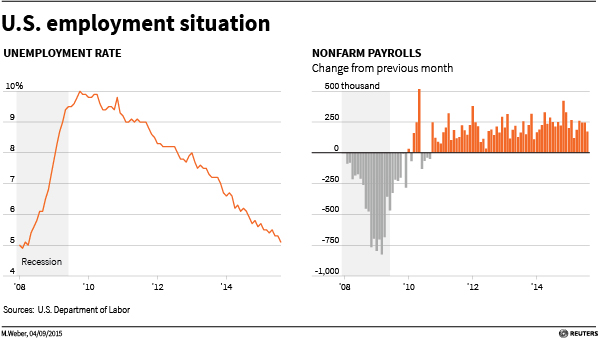
WASHINGTON, Oct 27 (Reuters) - Further falls in America's jobless rate will lead inflation to start rising early next year, according to a forecast based on research Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen has cited as shaping her confidence a rate hike could be needed this year.
Yellen has recently faced a rebellion at the central bank, with two Fed governors arguing that rate hikes should be delayed because of a breakdown in the tendency of low unemployment to fuel faster inflation, a relationship called the Phillips curve.
Governor Lael Brainard said this month that the Phillips curve relationship was "at best, very weak at the moment" while Daniel Tarullo said it has not been "operating effectively for 10 years now."
With the Fed's rate-setting committee meeting on Tuesday and Wednesday, Yellen and Vice Chair Stanley Fischer may seek to show the bank should not wait for inflation to appear before hiking rates. Both Yellen and Fischer have backed the relationship between jobs and inflation.
"The Phillips curve is alive and well," said Robert Gordon, an academic at Northwestern University whose 2013 paper on the subject was cited by Yellen and Fischer in speeches this year.
Gordon said the key reading to watch for signs of inflation was the short-term unemployment rate, those out of work less than six months, rather than the overall jobless rate. The relationship between that short-term joblessness and prices has held for 50 years, he said.
The short-term rate appears to matter because businesses set wages based on plausible candidates for a job, so the surge in people out of work for long spells since the recession might not influence inflation.
The short-term jobless rate has sunk to 3.7 percent, which is lower than it was at the outset of the 2007-09 recession. The overall unemployment rate is currently 5.1 percent.
Gordon's projection is that the short-term rate will sink to 3.5 percent by the end of 2016 and 3.3 percent by early 2017.
Inflation excluding food and energy, currently at 1.3 percent, would start slowly in the first quarter of 2016, with overall inflation rising from its current 0.3 percent rate to the Fed's 2 percent target by 2020, Gordon said.
Many Fed policymakers actually expect inflation will rise more quickly, so Gordon's projections are not an argument for the Fed to more aggressively head off price increases.
They do, however, shed light on why the Yellen and others at the Fed are confident inflation will rise.
"Considerable historical evidence suggests that inflation will eventually begin to rise as resource utilization continues to tighten," Yellen said in a March speech in which she cited Gordon's paper as supporting her belief in the Phillips curve.
Fischer cited Gordon's paper in August at the Fed's Jackson Hole conference, arguing the labor market played "at least some ongoing role" in determining inflation even though import prices can mask inflationary pressure created by employment.
Gordon's projections do not consider the chance a global economic slowdown could increase joblessness and stop inflation dead in its tracks, or that a decline in imported oil prices could keep inflation low.
But inflation could be expected to accelerate whenever the short-term rate was below 3.9 percent, which Gordon estimated would correspond to a total unemployment rate of 5.3 percent.
-------------------------
http://www.econlib.org/
The Phillips curve represents the relationship between the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate. Although he had precursors (phụ trách trước), A. W. H. Phillips’s study of wage inflation and unemployment in the United Kingdom from 1861 to 1957 is a milestone in the development of macroeconomics. Phillips found a consistent inverse relationship: when unemployment was high, wages increased slowly; when unemployment was low, wages rose rapidly.
Tìm được bằng chứng mối quan hệ giữa thất nghiệp và tiền lương, theo đó, thất nghiệp cao, tường lương tăng chậm; khi thất nghiệp thấp, tiền lương tăng nhanh chóng.
Phillips conjectured (mô phỏng, phỏng đoán)that the lower the unemployment rate, the tighter the labor market and, therefore, the faster firms must raise wages to attract scarce (khan hiếm) labor. At higher rates of unemployment, the pressure abated (dịu bớt). Phillips’s “curve” represented the average relationship between unemployment and wage behavior over the business cycle. It showed the rate of wage inflation that would result if a particular level of unemployment persisted (dai dẳng)for some time.
Economists soon estimated Phillips curves for most developed economies. Most related general price inflation, rather than wage inflation, to unemployment. Of course, the prices a company charges are closely connected to the wages it pays. Figure 1 shows a typical Phillips curve fitted to data for the United States from 1961 to 1969. The close fit between the estimated curve and the data encouraged many economists, following the lead of Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow, to treat the Phillips curve as a sort of menu of policy options. For example, with an unemployment rate of 6 percent, the government might stimulate the economy to lower unemployment to 5 percent. Figure 1 indicates that the cost, in terms of higher inflation, would be a little more than half a percentage point. But if the government initially faced lower rates of unemployment, the costs would be considerably higher: a reduction in unemployment from 5 to 4 percent would imply more than twice as big an increase in the rate of inflation—about one and a quarter percentage points.
Các nhà kinh tế nhận thấy mối quan hệ giữa lạm phát giá cả và thất nghiệp quan hệ mật thiết hơn cả tiền lương và thất nghiệp ở những quốc gia phát triển.
At the height of the Phillips curve’s popularity as a guide to policy, Edmund Phelps and Milton Friedman independently challenged its theoretical underpinnings. They argued that well-informed, rational employers and workers would pay attention only to real wages—the inflation-adjusted purchasing power of money wages. In their view, real wages would adjust to make the supply of labor equal to the demand for labor, and the unemployment rate would then stand at a level uniquely associated with that real wage—the “natural rate” of unemployment.
Figure 1 The Phillips Curve, 1961–1969

Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Note: Inflation based on the Consumer Price Index.
Both Friedman and Phelps argued that the government could not permanently trade higher inflation for lower unemployment. Imagine that unemployment is at the natural rate. The real wage is constant: workers who expect a given rate of price inflation insist that their wages increase at the same rate to prevent the erosion of their purchasing power. Now, imagine that the government uses expansionary monetary or fiscal policy in an attempt to lower unemployment below its natural rate. The resulting increase in demand encourages firms to raise their prices faster than workers had anticipated. With higher revenues, firms are willing to employ more workers at the old wage rates and even to raise those rates somewhat. For a short time, workers suffer from what economists call money illusion: they see that their money wages have risen and willingly supply more labor. Thus, the unemployment rate falls. They do not realize right away that their purchasing power has fallen because prices have risen more rapidly than they expected. But, over time, as workers come to anticipate higher rates of price inflation, they supply less labor and insist on increases in wages that keep up with inflation. The real wage is restored to its old level, and the unemployment rate returns to the natural rate. But the price inflation and wage inflation brought on by expansionary policies continue at the new, higher rates.
Friedman’s and Phelps’s analyses provide a distinction between the “short-run” and “long-run” Phillips curves. So long as the average rate of inflation remains fairly constant, as it did in the 1960s, inflation and unemployment will be inversely related. But if the average rate of inflation changes, as it will when policymakers persistently try to push unemployment below the natural rate, after a period of adjustment, unemployment will return to the natural rate. That is, once workers’ expectations of price inflation have had time to adjust, the natural rate of unemployment is compatible with any rate of inflation. The long-run Phillips curve could be shown on Figure 1 as a vertical line above the natural rate. The original curve would then apply only to brief, transitional periods and would shift with any persistent change in the average rate of inflation. These long-run and short-run relations can be combined in a single “expectations-augmented” Phillips curve. The more quickly workers’ expectations of price inflation adapt to changes in the actual rate of inflation, the more quickly unemployment will return to the natural rate, and the less successful the government will be in reducing unemployment through monetary and fiscal policies.
The 1970s provided striking confirmation of Friedman’s and Phelps’s fundamental point. Contrary to the original Phillips curve, when the average inflation rate rose from about 2.5 percent in the 1960s to about 7 percent in the 1970s, the unemployment rate not only did not fall, it actually rose from about 4 percent to above 6 percent.
Most economists now accept a central tenet of both Friedman’s and Phelps’s analyses: there is some rate of unemployment that, if maintained, would be compatible with a stable rate of inflation. Many, however, call this the “nonaccelerating inflation rate of unemployment” (NAIRU) because, unlike the term “natural rate,” NAIRU does not suggest that an unemployment rate is socially optimal, unchanging, or impervious to policy.
A policymaker might wish to place a value on NAIRU. To obtain a simple estimate, Figure 2 plots changes in the rate of inflation (i.e., the acceleration of prices) against the unemployment rate from 1976 to 2002. The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is the straight line that best fits the points on the graph (the regression line). It summarizes the rough inverse relationship. According to the regression line, NAIRU (i.e., the rate of unemployment for which the change in the rate of inflation is zero) is about 6 percent. The slope of the Phillips curve indicates the speed of price adjustment. Imagine that the economy is at NAIRU with an inflation rate of 3 percent and that the government would like to reduce the inflation rate to zero. Figure 2 suggests that contractionary monetary and fiscal policies that drove the average rate of unemployment up to about 7 percent (i.e., one point above NAIRU) would be associated with a reduction in inflation of about one percentage point per year. Thus, if the government’s policies caused the unemployment rate to stay at about 7 percent, the 3 percent inflation rate would, on average, be reduced one point each year—falling to zero in about three years.
Using similar, but more refined, methods, the Congressional Budget Office estimated (Figure 3) that NAIRU was about 5.3 percent in 1950, that it rose steadily until peaking in 1978 at about 6.3 percent, and that it then fell steadily to about 5.2 by the end of the century. Clearly, NAIRU is not constant. It varies with changes in so-called real factors affecting the supply of and demand for labor such as demographics, technology, union power, the structure of taxation, and relative prices (e.g., oil prices). NAIRU should not vary with monetary and fiscal policies, which affect aggregate demand without altering these real factors.
Figure 2 The Expectations-Augmented Phillips Curve, 1976–2002

Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Note: Inflation based on the Consumer Price Index.
The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is a fundamental element of almost every macroeconomic forecasting model now used by government and business. It is accepted by most otherwise diverse schools of macroeconomic thought. Early new classical theories assumed that prices adjusted freely and that expectations were formed rationally—that is, without systematic error. These assumptions imply that the Phillips curve in Figure 2 should be very steep and that deviations from NAIRU should be short-lived (see new classical macroeconomics and rational expectations). While sticking to the rational-expectations hypothesis, even new classical economists now concede that wages and prices are somewhat sticky. Wage and price inertia, resulting in real wages and other relative prices away from their market-clearing levels, explain the large fluctuations in unemployment around NAIRU and slow speed of convergence back to NAIRU.
Figure 3 Nonaccelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment

Source: Congressional Budget Office.
Some “new Keynesian” and some free-market economists hold that, at best, there is only a weak tendency for an economy to return to NAIRU. They argue that there is no natural rate of unemployment to which the actual rate tends to return. Instead, when actual unemployment rises and remains high for some time, NAIRU also rises. The dependence of NAIRU on actual unemployment is known as the hysteresis hypothesis. One explanation for hysteresis in a heavily unionized economy is that unions directly represent the interests only of those who are currently employed. Unionization, by keeping wages high, undermines the ability of those outside the union to compete for employment. After prolonged layoffs, employed union workers may seek the benefits of higher wages for themselves rather than moderating their wage demands to promote the rehiring of unemployed workers. According to the hysteresis hypothesis, once unemployment becomes high—as it did in Europe in the recessions of the 1970s—it is relatively impervious to monetary and fiscal stimuli, even in the short run. The unemployment rate in France in 1968 was 1.8 percent, and in West Germany, 1.5 percent. In contrast, since 1983, both French and West German unemployment rates have fluctuated between 7 and 11 percent. In 2003, the French rate stood at 8.8 percent and the German rate at 8.4 percent. The hysteresis hypothesis appears to be more relevant to Europe, where unionization is higher and where labor laws create numerous barriers to hiring and firing, than it is to the United States, with its considerably more flexible labor markets. The unemployment rate in the United States was 3.4 percent in 1968. U.S. unemployment peaked in the early 1980s at 10.8 percent and fell back substantially, so that by 2000 it again stood below 4 percent.
Modern macroeconomic models often employ another version of the Phillips curve in which the output gap replaces the unemployment rate as the measure of aggregate demand relative to aggregate supply. The output gap is the difference between the actual level of GDP and the potential (or sustainable) level of aggregate output expressed as a percentage of potential. This formulation explains why, at the end of the 1990s boom when unemployment rates were well below estimates of NAIRU, prices did not accelerate. The reasoning is as follows. Potential output depends not only on labor inputs, but also on plant and equipment and other capital inputs. At the end of the boom, after nearly a decade of rapid investment, firms found themselves with too much capital. The excess capacity raised potential output, widening the output gap and reducing the pressure on prices.
Many articles in the conservative business press criticize the Phillips curve because they believe it both implies that growth causes inflation and repudiates the theory that excess growth of money is inflation’s true cause. But it does no such thing. One can believe in the Phillips curve and still understand that increased growth, all other things equal, will reduce inflation. The misplaced criticism of the Phillips curve is ironic since Milton Friedman, one of the coinventors of its expectations-augmented version, is also the foremost defender of the view that “inflation is always, and everywhere, a monetary phenomenon.”
The Phillips curve was hailed in the 1960s as providing an account of the inflation process hitherto missing from the conventional macroeconomic model. After four decades, the Phillips curve, as transformed by the natural-rate hypothesis into its expectations-augmented version, remains the key to relating unemployment (of capital as well as labor) to inflation in mainstream macroeconomic analysis.
About the Author
Kevin D. Hoover is professor in the departments of economics and philosophy at Duke University. He is past president of the History of Economics Society, past chairman of the International Network for Economic Method, and editor of the Journal of Economic Methodology.
Further Reading
Cross, Rod, ed. Unemployment, Hysteresis, and the Natural Rate Hypothesis. Oxford: Blackwell, 1988.
Friedman, Milton. “The Role of Monetary Policy.” American Economic Review 58, no. 1 (1968): 1–17.
Lucas, Robert E. Jr. “Econometric Testing of the Natural Rate Hypothesis.” In Otto Eckstein, ed., The Econometrics of Price Determination. Washington, D.C.: Federal Reserve System, 1972.
Phelps, Edmund S. “Phillips Curves, Expectations of Inflation and Optimal Employment over Time.” Economica, n.s., 34, no. 3 (1967): 254–281.
Phillips, A. W. H. “The Relation Between Unemployment and the Rate of Change of Money Wage Rates in the United Kingdom, 1861–1957.” Economica, n.s., 25, no. 2 (1958): 283–299.
Samuelson, Paul A., and Robert M. Solow. “Analytical Aspects of Anti-inflation Policy.” American Economic Review 50, no. 2 (1960): 177–194.
Sheffrin, Steven M. Rational Expectations. 2d ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996.
Symposium: “The Natural Rate of Unemployment.” Journal of Economic Perspectives 11, no. 1 (1997): 3–108.
Source: finandlife|economicshelp|Reuters|http://www.econlib.org/