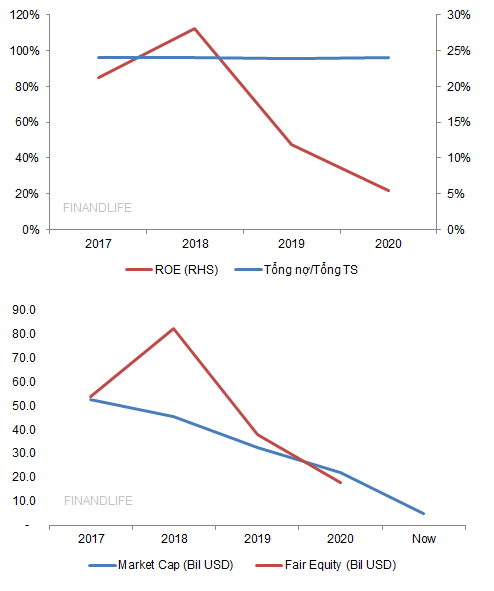
China Evergrande Group thường xuyên duy trì đòn cân nợ lên đến 98% trên tổng tài sản, trong đó nợ vay ngân hàng thường xuyên vượt 5 lần vốn chủ sở hữu.
ROE những năm đầu rất cao, năm 2017 đạt 21%, năm 2018 đạt 28%. Vốn hóa thị trường những năm này duy trì ở 45-55 tỷ USD. Đến 2019, ROE tụt xuống còn 12%; năm 2020 chỉ còn 5%. Kể từ đó, vốn hóa thị trường rớt không phanh, đến nay chỉ còn quanh 5 tỷ USD, tức đã mất 90% giá trị so với 3-4 năm trước.
Điều kỳ lạ là tại sao một doanh nghiệp bất động sản lại được sử dụng đòn bẩy cao như vậy? Tại sao nhà bank và người dân dám cho Công ty này vay nợ?
Link bài đọc định nghĩa về WMP
FINANDLIFE
=====
Liệu Evergrande có tạo ra đợt vỡ nợ lây lan kiểu Lehman moment ở Trung Quốc?
Hồ Quốc Tuấn
Đến lúc này dân tình vẫn thật ra không ai rõ qui mô vỡ nợ tiềm tàng của Evergrande sẽ là bao nhiêu? Ổng trả được bao nhiêu và thiếu bao nhiêu.
Con số tạm thời cần tái cấu trúc là 300 tỷ đô, nhưng sẽ còn bao nhiêu nữa (nhớ Hy Lạp hôn mấy bạn, sau lần 1 là lần 2, và sau đó là lần … 3, 4, 5).
Vấn đề không phải chỉ là ở Evergrande và hơn 70 nghìn nhà đầu tư mua dự án của Evergrande bị kẹp hàng, mà là mấy chục nghìn công ty bất động sản khác ở cả Trung Quốc, như chúng ta hay hiểu là tác động lây lan.
Concern over Evergrande’s ability to make good on $300 billion of liabilities is spilling into China’s financial markets. Shares of other real estate firms have plunged
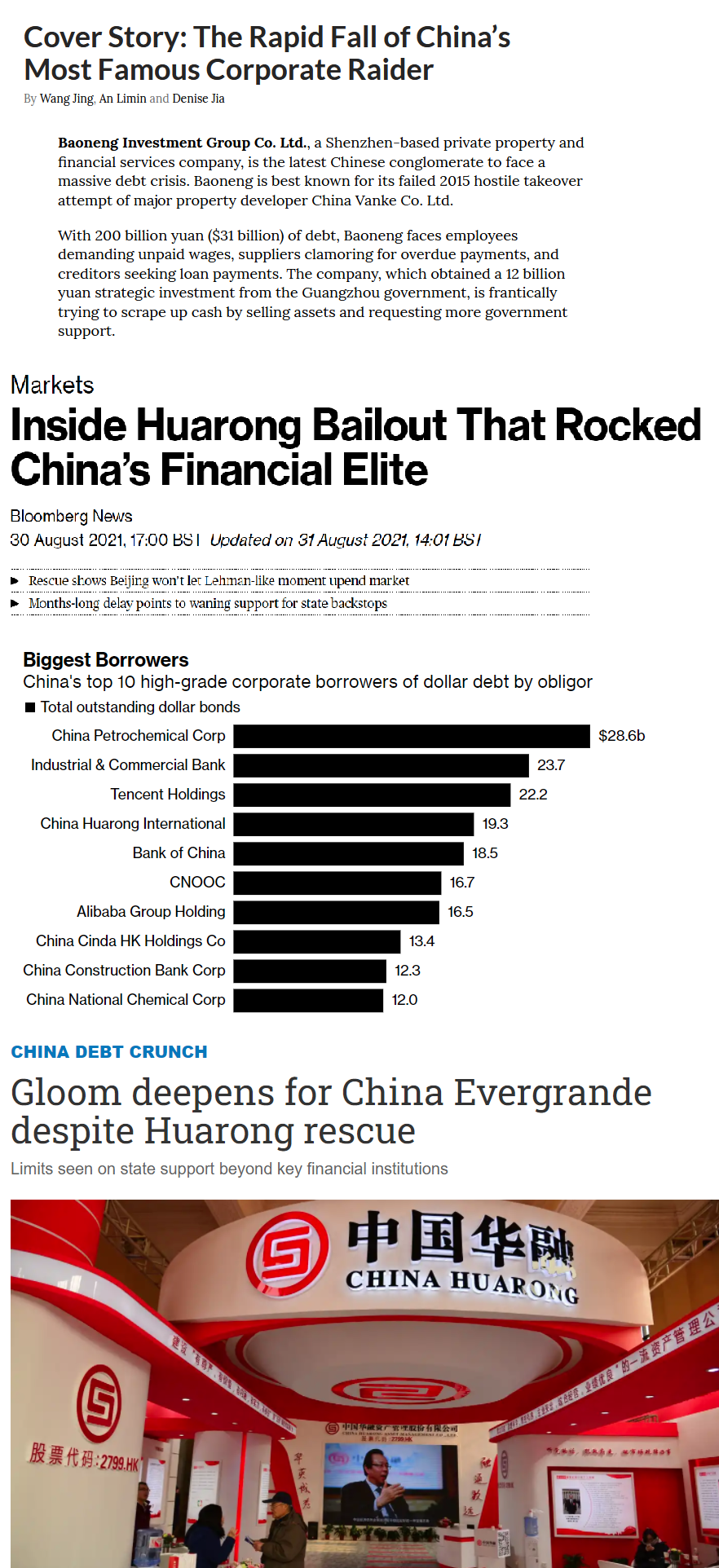
Trong khi bà con chỉ chú ý Evergrande, đã có những trường hợp nhỏ hơn đang sập. Ví dụ trường hợp Baoneng Investment với chỉ 31 tỷ đô nợ. Và chính quyền Quảng Châu đang nhảy vào cứu, bơm cho 12 tỷ tiền vốn “đầu tư chiến lược”. Cụ này giống như Evergrande, đang ráng bán tài sản để mà trả nợ, nhưng fire sales thì dân bảo là đang sale off 25% everywhere nên anh muốn tui mua thì sale off 50% đi. Người có tiền không gấp.
Toàn bộ supply chain bị dính vào đợt bán sale off mùa thu này đang được ước tính chiếm khoảng hơn 1/4 qui mô nền kinh tế Trung Quốc. Bà con cứ chém gió Trung Quốc sản xuất, tech gì gì, thiệt ra vẫn là bán nhà sống thôi.
Fire sales pummel an already shaky real estate market, squeezing other developers and rippling through a supply chain that accounts for more than a quarter of Chinese economic output.
Bà con đang chú ý đến Evergrande mà không để ý tháng rồi Trung Quốc đã cứu Huarong và vụ đó đã dẫn đến rạn nứt nghiêm trọng trong nội bộ cố vấn của Trung Quốc.
Nay thì Evergrande đặt các lãnh đạo vào thế khó.
Huarong qui mô quá lớn và là con ruột, không thể không cứu. Nhưng Evergrande lại là câu chuyện khác.
Nếu như cứu Huarong là vì qui mô phát hành nợ quốc tế, vai trò con ruột cũng như tính chất là cờ đầu của Huarong trong lĩnh vực asset management của Nhà nước, thì Evergrande là con ghẻ ngoài phố. Và cứu Evergrande có thể dẫn đến nhiều ông không tích cực xử lý tài sản mà cứ lăn đùng ra xin cứu.
Nikkei Asia đã cảnh báo vụ này hồi tháng 8 khi Huarong được cứu, cảnh báo Huarong được cứu không có nghĩa là Evergrande sẽ được cứu.
Câu này của Bloomberg chốt hạ vấn đề của Trung Quốc: Đảng Cộng Sản sẽ chấp nhận chịu đau đến đâu. Đặc biệt nhấn mạnh chứ “financial contagion”.
While it’s impossible to know for sure what would happen if Beijing allows Evergrande’s downward spiral to continue unabated, China watchers are gaming out worst-case scenarios as they contemplate how much pain the Communist Party is willing to tolerate. Pressure to intervene is growing as signs of financial contagion increase.
Nếu lãnh đạo kiên trì bảo như kiểu “dịch lây thế nào được, tháng 8 sẽ dập được dịch”, Trung Quốc có thể mắc sai lầm, để xảy ra Lehman moment thì lãnh đạo đương nhiệm sẽ gánh tội.
Nếu cứu quá tay, thì chính lãnh đạo đương nhiệm cũng bị chỉ trích.
Năm sau Đại hội Đảng,mà nguồn lực của Trung Quốc không phải vô hạn, trong khi số zombie cần cứ thì rất đông. Chọn ai được cứu, ai không được cứu là rất khó. Quan trọng là không biết con zombie nào không cứu nó lăn đùng ra thì lan tràn dịch zombie khắp nơi.
Con zombie Evergrande này không đơn giản ở chỗ là nó dính tùm lum. Ngoài việc nó kẹp 70,000 nhà đầu tư mua nhà, nó có thể kẹp không ít tổ chức nước ngoài mua trái phiếu. Đồng thời với số hàng Evergrande đang có trong tay, nếu quăng ra thị trường bán fire-sale, thị trường bất động sản Trung Quốc sẽ rúng động.
Evergrande is the largest high-yield dollar bond issuer in China, accounting for 16% of outstanding notes, according to Bank of America Corp. analysts. Should the company collapse, that alone would push the default rate on the country’s junk dollar bond market to 14% from 3%, they wrote in a note this month.
While Beijing has become more comfortable with allowing weaker businesses to fail, an uncontrolled spike in offshore funding costs would risk derailing a key source of financing. It could also undermine global confidence in the country’s issuers at a time when Beijing is pushing for larger foreign investor ownership. Yields on China’s junk dollar bonds are nearing 14%, up from about 7.4% in February, according to a Bloomberg index.
“If Evergrande had to dump its inventory onto the market” it would “drag down property prices substantially,” said Hao Hong, chief strategist at Bocom International.
Quan trọng hơn là, nếu con này chết, không chừng một số ông đang tưởng khỏe mạnh ở Trung, Âu, Mỹ có khi tự nhiên lăn đùng ra. Các ông vay nợ rồi đem qua cho Evergrande vay mà. Và ai cho mấy ông đó vay thì có trời mới biết.
Câu này của Bloomberg độc: quá khứ 2015 chứng minh không phải cứ Bắc Kinh ra cứu là cứu được market dù chính phủ nắm hầu hết ngân hàng và có thể nắm được đủ thứ bên.
Yet a benign outcome is far from assured. Beijing’s bungled stock-market rescue in 2015 showed how difficult it can be for policy makers to control financial outcomes, even in a system where the government runs most of the banks and can exert outsized pressure on creditors, suppliers and other counterparties.
Quan trọng nhất là giờ các lãnh đạo cao nhất của Trung Quốc đến giờ vẫn chưa có chỉ đạo rõ ràng. Theo alô model của mình thì lãnh đạo của PBoC hiện cũng không khác gì lính cứu hỏa ở tiền tuyến. Sếp chỉ đạo bây cứ bơm chút nước khống chế lửa thì cứ bơm, chứ cũng không biết next move là gì. Mà có thể lãnh đạo của sếp PBoC cũng chưa biết mình muốn gì. Vì ổng có thể chưa biết ai sẽ là đồng minh hay kẻ thù của mình năm sau.
The People’s Bank of China injected $14 billion of short-term cash into the financial system on Friday in a sign policy makers want to soothe nerves.
Trong khi đó, vấn đề của Evergrande nói riêng hay đống ông phát triển nhà ở Trung Quốc nói chung có thể không chỉ là vấn đề của Trung Quốc.
A correction in China’s property market would not only slow the domestic economy but have global consequences too.
Có thể hiểu là giống như chống dịch, ai cũng nhìn thấy phong tỏa chống dịch thì sẽ chết kinh tế. Nhưng lãnh đạo có những tính toán khác. Nhưng lại tính thiếu là bài toán kinh tế nó có thể ảnh hưởng mấy bài toán khác. Khi giật mình nhìn lại có thể là đã muộn.
Nguồn tham khảo thêm
China’s Nightmare Evergrande Scenario Is an Uncontrolled Crash
Inside Huarong Bailout That Rocked China’s Financial Elite
Gloom deepens for China Evergrande despite Huarong rescue
Casinos and Evergrande Crisis Renew Worries Over China Stocks
Cover Story: The Rapid Fall of China’s Most Famous Corporate Raider
In Depth: The Never-Ending Battle to Curb China’s Hidden Debt
========
===
This Is How Contagion From Evergrande's Default Will Spread To The Rest Of The World
BY TYLER DURDEN
SUNDAY, SEP 19, 2021 - 04:55 PM
"There is probably no company that is more representative of the investment bubble than Evergrande. It s the biggest pyramid scheme the world has yet seen."
- Anne Stevenson-Yang, Aug 2017
Something historic will happen this week: as Beijing warned last week, China's largest and most indebted property developer, Evergrande, will default on some (or all) of its $313 billion in debt. And while some in the financial media are trying to talk down the significance of this event, make no mistake - this will be China's "Lehman moment", the only question is whether it will be controlled and contained, or will it be chaotic (i.e.m the "Nightmare Scenario" discussed on Thursday) and lead to worldwide contagion and a global deflationary shockwave. The answer will depend on how Beijing reacts and what it does in response.
In terms of immediate next steps, the sequence of events is well-known. Evergrande is due to pay $83.5 million of interest on Sept. 23 for its offshore March 2022 bond. It then has another $47.5 million interest payment due on Sept. 29 for March 2024 notes. The bonds will default if Evergrande fails to pay the interest within 30 days, and as shown in the chart below, it's only downhill from there. We now know that Evergrande will not pay the interest, nor will it pay upcoming principal maturities, meaning that a technical default is just a few days away.
Ahead of the coming default, which as Bloomberg notes is unhedgable for the simple reason that nobody wants to take exposure on Evergrande CDS in betting against a default which as recently as a month ago was unthinkable, the company's main lenders are quietly bracing for impact with Reuters reporting that banks are provisioning for substantial losses on loans to the embattled property developer, while some creditors are planning to give it more time to repay. According to the report, Agricultural Bank of China (AgBank) the country's No.3 lender by assets, has made some loan loss provisions for part of its exposure to Evergrande. At the same time, China Minsheng Banking and China CITIC Bank Corp, two other major Evergrande lenders, are prepared to roll over some of their near-term debt obligations, two separate sources with knowledge of each situation said.
The good news for local banks is that unlike most naive bondholders, they have been gradually trimming their exposure to Evercore ahead of the coming endgame which should have been obvious to anyone from a mile away (back in November 2017 we penned "Does Evergrande Mark The Beginning Of China's Minsky Moment?" the answer we now know is yes). Minsheng, for example, cut its loan exposure to Evergrande to 30 billion yuan from 40 billion yuan over the past 12 months. Last year, Evergrande reported total bank and other borrowings of 693.4 billion yuan ($107.4 billion) - including loans granted by trust firms rather than banks, which analysts said accounted for the bigger portion - down from 782.3 billion yuan in 2019.
Yet despite the retrenchment, an Evergrande collapse, even a controlled one, would still reverberate through the Chinese economy given liabilities equal to 2% of the country's GDP. It would cripple the embattled property sector, leading to a painful bond selloff among the rest of China's property developers, hammering China's real estate sector, which accounts for approximately 70% of Chinese household wealth as we showed back in 2014...
... and will result in a recession even in a best case scenario. That said, a "best case" scenario is unlikely: the company's bank exposure is wide and a leaked 2020 document, written off as a fabrication by Evergrande but taken seriously by analysts, showed liabilities extending to more than 128 banks and over 121 non-banking institutions.
After that leaked document, the People's Bank of China requested all main Evergrande lenders to review their loan exposure and assess relevant financial risks on a monthly-basis, a source at a state-owned bank told Reuters.
In other words, as Evergrande goes so goes China's financial system, and while this is China's "Lehman Moment", there is one difference: in China all banks are state-owned, which means that Beijing will be able to react directly and offset a Lehman-like deflationary shock, if it is so inclined: it will just cost it trillions in new stimulus to offset the deflationary collapse that the default of hundreds of billions in debt will entail.
Of course, Beijing could have taken steps to proactively avert a worst-case outcome, an outcome which even UBS admits it did not anticipate as recently as Aug 26 (meanwhile, we warned it was coming back in 2017) in a report from Sept 16 in which it admits...
"In our most recent note, we had highlighted that the notion "too big to fail" did still hold for higher quality SOE names, although we did not see Evergrande falling into this remit given the Chinese authorities' ongoing policy stance towards the property sector. That said, we did not see any imminent risk of a credit event occurring for Evergrande."
What changed UBS' mind (besides perhaps finally reading this website)? Nothing that we didn't already know, but here it is in UBS' own words:
1. Evergrande hiring financial advisors to explore feasible options to ease its liquidity woes,
2. Expectations for contracted sales to decline over the next 1-2m (Figure 1) and
3. A further lack of progress in terms of property and non-property asset disposals (Figure 2).
The bottom line, according to UBS is that "while the Chinese authorities have tried to intervene and ask banks to allow for payment extensions... the ability of Evergrande to generate sufficient liquidity in the near term through contracted sales and asset disposals has deteriorated considerably and in turn increased the likelihood of credit event occurring sooner rather than later."
This is also why anyone hoping that controlled asset sales in a liquidation context will somehow generate even modest recoveries for bondholders is delusional: an Evergrande default will not only drag down its peer developers, but will lead to the bottom falling out of the Chinese housing market, leading to a selling frenzy in a market where already some 65 million apartments were vacant, representing more than 21% of all homes in urban China.
A few more observations on the massive relative scale that the Evergrande "problem" represents. On Friday, following the latest news that a default is imminent, we showed that China's junk bond yields not just surged higher overnight, but have surpassed the March 2020 peak covid crisis highs, printing 14.34% overnight, and the highest level since the great repo rate crisis of 2011.
What was behind the move? As we said previously, "in a word - and the only word that matters - it's Evergrande, and while contagion is clearly present (finally, as investors realize that the $300 billion creditor is about to default) it really is mostly Evergrande. Consider the following stunning facts:
• Evergrande is the largest high-yield dollar bond issuer in China, accounting for 16% of outstanding notes, according to Bank of America. Should the company collapse, that alone would push the default rate on the country s junk dollar bond market to 14% from 3%.
• It's not just the dollar bond market: the stakes are even higher on the mainland, where as Bloomberg calculates, the yuan-denominated credit market is about 15 times the size at $12 trillion. While Evergrande is less of a whale onshore, a collapse would force banks to cut their holdings of corporate notes and even freeze money markets, the plumbing of China s financial system
It's also why on Friday, after months of pretending all is well, the PBOC injected a net 90 billion in liquidity into the system, the biggest repo injection since February, in response to a surge in the 7-day repo rate to the highest level since June.
Yes, contagion is starting, and should the credit crunch get much worse, the government or central bank would be forced to act. Banks involved in property lending may come under pressure, leading to an increase in soured loans. Smaller banks exposed to Evergrande or other weaker developers may face significant increases in non-performing loans in the event of a default, according to Fitch Ratings.
* * *
Drilling down into the critical topic of contagion, we have two distinct vectors - domestic and international. As UBS expands, for the Chinese property sector, the offshore financing channel consists of the offshore bond market (USD-denominated), offshore syndicated loan and private deal financing. The offshore bond market is the biggest in size (and where data is most readily available), with total debt outstanding currently at ~$209bn, ~70% of which is HY rated.
Based on UBS estimates that the total liability of the Chinese property sector is close to $4.7trn, the offshore bond market therefore only accounts for only 4.5% of total financing for the sector. And since Evergrande's total liability size is ~$313 billion, it represents 6.5% of the total liability of the Chinese property sector. In terms of total offshore bonds outstanding, UBS calculates that Evergrande has ~$19bn, which is equivalent to roughly 9% of the total offshore bond market and 12% of the total HY offshore bond market (slightly below BofA's estimate of 16%). Other high beta B-rated property developer names make up a further ~12.5% of the total HY offshore bond market, which is important given the the high correlation between these names and the Evergrande price action.
While Beijing has become more comfortable with allowing weaker businesses to fail, an uncontrolled spike in offshore funding costs would risk derailing a key source of financing. It could also undermine global confidence in the country s issuers at a time when Beijing is pushing for larger foreign investor ownership. As shown above, yields on China s junk dollar bonds are nearing 14%, up from about 7.4% in February, largely due to the crash in Evergrande debt.
Having quantified the exposure, the next question is what is the potential domestic contagion. Here we will repeat some of the salient points we brought up earlier this week when discussing China's "Nightmare Scenario":
Social Unrest - Maintaining social order has always been a key priority for the Communist Party, which has no tolerance for protests of any kind. In Guangzhou, homebuyers surrounded a local housing bureau last week to demand Evergrande restart stalled construction. Disgruntled retail investors have gathered at the company s Shenzhen headquarters for at least three straight days this week, and videos of protests against the developer in other parts of China have been shared widely online (see video above). Without a social safety net and with limited places to put their money, Chinese savers have for years been encouraged to buy homes whose prices were only ever supposed to go up (similar to the US before 2007 when even idiots like Ben Bernanke said that the US housing market never goes down). Today, buying a house (or two) is a cultural touchstone. While housing affordability has become a hot topic in the
West, many Chinese are more likely to protest falling home prices than spiking ones.
Given that the bulk of people s wealth is already in property, even a 10% correction would be a serious knock to many people, said Fraser Howie, an independent analyst and co-author of books on Chinese finance who has been following the country s corporate sector for decades. It would certainly knock their hopes and dreams and expectations about what property is.
Shadow banks: Another potential flashpoint is whether Evergrande can repay high-yield wealth management products that it sold to thousands of retail investors, including many of its own employees. About 40 billion yuan of the WMPs are due to be repaid, according to Caixin, a Chinese financial news service. Evergrande is trying to free up cash by selling assets, including stakes in its electric-car and property-management businesses, but has so far made little progress.
Capital Markets: Evergrande is the largest high-yield dollar bond issuer in China, accounting for 16% of outstanding notes, according to Bank of America. Should the company collapse, that alone would push the default rate on the country s junk dollar bond market to 14% from 3%. While Beijing has become more comfortable with allowing weaker businesses to fail, an uncontrolled spike in offshore funding costs would risk derailing a key source of financing. It could also undermine global confidence in the country s issuers at a time when Beijing is pushing for larger foreign investor ownership. Yields on China s junk dollar bonds are nearing 14%, up from about 7.4% in February, according to a Bloomberg index, largely due to the crash in Evergrande debt.
Economic Impact: Concern over Evergrande comes at a time when China s economy is slowing sharply. Aggressive controls to curb outbreaks of Covid-19 are hurting retail spending and travel, while measures to cool property prices are taking a toll. Data this week showed home sales by value slumped 20% in August from a year earlier, the biggest drop since the onset of the coronavirus early last year. Responding to a question on Evergrande s potential impact on the economy, National Bureau of Statistics spokesman Fu Linghui said some large property enterprises are running into difficulties and the fallout remains to be seen.
China s current priorities of promoting common prosperity and deterring excessive risk-taking mean there s unlikely to be any easing of property curbs this year, according to Macquarie Group Ltd. The sector will be a main growth headwind for next year, although policy makers may loosen restrictions to defend growth goals, Macquarie analysts wrote in a Wednesday note.
A crash in China s property market would not only slow the domestic economy but have global consequences too.
A significant slowdown in property construction over the next few years appears probable already, and would become even more likely in the event of an Evergrande failure or bankruptcy, said Logan Wright, a Hong Kong-based director at research firm
Rhodium Group LLC. A long-term slowdown in property construction, an industry that represents around a fifth or a quarter of China s economy by most estimates, would cause a significant decline in GDP growth, commodity demand, and would likely have disinflationary effects globally.
* * *
Which brings us to the $313 billion question: what would cause the Evergrande default to spill over into global markets?
First, let's back up a bit: while domestic contagion is assured, Beijing's response is even more critical. We won't go into details here, suffice to say that an obvious escape valve is for Beijing to activate trillions in new "emergency credit" to offset the deflationary tsunami". In fact, to those of a cynical bent, one can almost say the whole thing is staged, and just as covid was the trigger for the $40 trillion fiscal/monetary stimulus cycle of 2020-2021, the Evergrande collapse will be the catalyst for a similar if not bigger stimulus in 2022-2023.
Covid was to the $40 trillion fiscal/monetary stimulus cycle of 2020-2021 as Evergrande collapse/China real estate crisis will be to 2022-2023
zerohedge (@zerohedge) September 17, 2021
Cynicism aside, in discussing this critical escalation, UBS writes that while its base case (now) is that a credit event for Evergrande is unavoidable," the extent to which we get spill over into other markets will be contingent on whether Evergrande restructures or fully liquidates" and, naturally, UBS adds that "as of today, we remain confident that the former is a much more probable outcome", then again the very same UBS just three weeks ago predicted that an event of default was unlikely to happen. Maybe the largest Swiss bank should stop making predictions? Of course it won't, so here is what it thinks will happen (this is the optimistic case): Current pricing of the 2025 bonds at $27 (implying a recovery rate of 25-30%) with the current discount reflecting a haircut for Evergrande's weaker balance sheet, thin trading liquidity and some risk premium associated with a full liquidation.
In the event of a restructuring, UBS expects the bonds to bounce off their lows and contagion to be broadly limited, but in the event of a full liquidation, the Swiss bank does concede that it's going to get very mess, and expects to see a high degree of contagion via three key channels (for those pressed for time, this is the bulletin punchline of this article):
1. Investors getting extremely low recovery values, something which would lead to a material loss of investor confidence in the broader property sector/Asia HY offshore market and create spill over into the broader Chinese financial assets. We saw this play out the Baoshang bank bankruptcy last year, where a liquidity squeeze in the interbank market was caused by banks cut off their lending to non-bank institutions and small banks. This consequently led a sell-off in local rates in China. This could cause also lead to a repricing of risk premium across global credit markets, with EM underperforming DM and HY-IG decompression in both USD/EUR markets.
2. A domino effect of credit events, given that both banks and non-banks with large exposures to Evergrande could potentially go under or be forced into restructuring. This would again create spill over into other Chinese financial assets and drive underperformance of financials in particular across both DM and EM credit/equity markets, led by those names with direct exposure either to Evergrande itself, its subsidiaries or its creditors. Evergrande's liabilities are said to involve more than ~130 banks and over ~120 non-banking institutions, while the developer also hires 4 million people every year for project developments, something which could also lead to increased investor concerns around financial stability risks in China.
3. A full liquidation would involve Keepwell Agreements not being adhered to something which will force rating agencies to recalibrate their methodologies and remove multiple rating uplifts and assumptions of state support across non-property sectors both within the offshore USD market as well as the onshore market. This could lead to added selling pressure and drive large liquidity distortions across both Chinese offshore and onshore bond markets, with potential for spillover into EM credit, given that several EM credit accounts do tend to hold Chinese offshore bonds as a part of their Asia HY exposure.
Similar to UBS, one month ago Goldman Sachs also said not to worry about Evergrande. Oops.
In a note last week from the bank's China analyst Kenneth Ho titled "Reassessing Contagion Risk from Evergrande Concerns" (available for professional subscribers in the usual place), the bank notes that in light of the latest dire news, "we revisit our assessment on the potential contagion impact from Evergrande concerns" and notes that two factors will drive any potential spillover effects towards the broader credits and to the economy:
1. Disruptions to the onshore property development operations. The company has acknowledged that ongoing negative media reports have dampened the confidence of potential property purchasers, contributing to the recent falls in contract sales. Furthermore, Caixin reported that hundreds of investors gathered at the company s headquarters in Shenzhen earlier this week due to the missed payments for the WMPs. These suggest that further disruptions to the company s property development operations can be very negative for sentiment amongst domestic property buyers and investors, and potentially spill over to the broader property sector. Possible options in such a situation could include a restructuring to ensure the onshore operations continue (e.g., bringing in third parties to invest in the company and stabilize operations there have been examples of similar occurrences in the past) and also considering potential debt and equity restructuring. If the onshore property operations can continue as a going concern, that could have less scope for contagion impact, but that would mean Beijing will dilute its deleveraging vow again.
2. Offshore recovery prospects relative to current bond prices. The other factor that could impact offshore bond market sentiment is recovery prospects under a debt restructuring. With the EVERRE bonds priced around mid-20s and the TIANHL bonds just below 20, the contagion impact may be limited if potential restructuring prospects were close to current market levels. In calculating recoveries, note that the EVERRE bonds are issued by the offshore parent company with guarantees from a number of the company s offshore subsidiaries, whilst the TIANHL bonds are issued by an offshore special purpose vehicle (SPV), with offshore subsidiary guarantees and credit support from a keepwell agreement and equity interest purchase undertaking (EIPU) from Hengda Real Estate (Exhibit 1). These suggest that recoveries in a potential restructuring could differ between the two sets of offshore bonds given the structural differences, and that any potential restructuring process may be prolonged.
Which brings us to the obligary org chart, which bondholders will soon get to know by heart as they push for higher recoveries. The good news: it is nowhere near as complicated as Enron.
What follows next is a rather lenghty discussion of the recovery prospects for EVERRE (offshore) and TIANHL (onshore) bonds. For those who are not currently involved in the org structure, are not creditors or Evergrande, or are simply not interested in the nuances, we suggest you skip to the conclusion.
EVERRE bonds recovery prospects
Assessing holding company level indebtedness. The $14.0bn of EVERRE offshore bonds are issued by the parent company, with a number of offshore subsidiaries acting as guarantors (see org chart above). Therefore, to assess the potential recovery, one needs to assess the amount of indebtedness at the parent company level and the value of the parent company s investments. Alas, as Goldman notes, that cannot be accurately ascertained, as Evergrande provides financial results on a consolidated basis, with the most recent financial results from June 2021. However, we are able to obtain financial results from a number of their consolidated subsidiary companies, including Hengda Real Estate (the 59.4% owned onshore property development company, which is also their main operating entity) and two of their listed consolidated subsidiaries (China Evergrande New Energy Vehicle and Evergrande Property Services Group). This allows us to map out the distribution of Evergrande s total debt, which totaled RMB 571.8bn ($88.6bn) at the end of June 2021.
Assuming potential $21.5bn of debt at the holdco level. Exhibit 2 provides an estimated breakdown of Evergrande s total debt. In additional to the $14.0bn of EVERRE bonds, there is an RMB 8.2bn ($1.3bn) onshore bond issued by Hengda Real Estate (EVERCN 6.98% 8 Jul 2022) that has a repurchase agreement by the parent company. The rest of the indebtedness can be attributed to the various subsidiary companies, with the exception for an amount totaling $6.2bn of debts, which we term Other debts . If we conservatively assume that the $6.2bn of other debts and the RMB 8.2bn onshore bond are both parent company level debts, we arrive at a potential total amount of indebtedness at the parent company level at $21.5bn. Note that we do not assume any of the Hengda bank and trust loans have guarantees by the parent company. Based on Hengda Real Estate s latest financial report, it does not state any of their indebtedness as guaranteed by the parent company.
Lots of unknowns, therefore caution is warranted. Given the complexity of Evergrande Group, and the lack of sufficient information on the company s assets and liabilities, it is difficult to ascertain a more precise picture of the recovery prospects. On the positive side, there are other assets that could provide additional value, and the chart below provides a basic breakdown of the assets of China Evergrande Group and their major consolidated subsidiaries. On the negative side, there is the all too realistic possibility of additional liabilities we have not incorporated, such as off balance sheet items. For example, on a fully consolidated basis, the company has provided financial guarantees (excluding mortgage facilities) totaling RMB 29.5 at the end of 2020, of which RMB 23.7 were provided by Hengda Real Estate. This suggests there could potentially be guarantees provided at the parent company level. All in all, given the uncertainties, much caution is warranted.
TIANHL bond recovery depends on Hendga Real Estate operations... One aspect of the recovery prospects for the $5.2bn of TIANHL bonds outstanding is the strength of the operations of Hengda Real Estate. In terms of book leverage (i.e., total debt divided by total debt plus book equity), Hengda Real Estate was at 56.0% at the end of June 2021, which is near the median level for China Property HY issuers. That said, the balance sheet is likely far more levered than indicated by the book leverage. The chart below lays out the balance sheet for Hengda Real Estate at the end of June 2021, and it indicates the company having RMB 755.9bn of trade payables and other current liabilities, rising from RMB 651.7bn at the end of December 2020. That tightness in onshore liquidity and in the credit markets meant that the company may have had to extend payment terms to their suppliers. Therefore, if one incorporates part of the payables as debt, the book leverage would increase substantially. For example, if 100% of the trade payables and other current liabilities are incorporated as debt, the book leverage would increase to 77.8%, and if 50% are included then it would rise to 70.5%.
...as well as the strength of the keepwell agreement. In addition to the uncertainties surrounding the leverage at Hengda Real Estate, there are uncertainties regarding the structure of the TIANHL bonds. As shown in the org chart above, the TIANHL bonds are issued by an offshore special purpose vehicle (SPV), with credit support from a keepwell agreement and equity interest purchase undertaking (EIPU) from Hengda Real Estate. Yes, when analysts figure out that they've put their money into yet another Chinese SPV, their heads will spin come Monday when they actually start reading this stuff. The strength of the keepwell and EIPU structure is unclear, and in our previous report, we assumed recovery prospects for keepwell structure bonds to be 50% below that for senior unsecured debt of the same entity.
Much will depend on the debt structure for Hengda. At the end of June 2021, Hengda Real Estate had RMB 405.5bn ($62.8bn) of debt outstanding, of which RMB 270.8bn ($42.0bn), or 66.8% of the debts, are secured borrowings (Exhibit 6). Another RMB 39.3bn of debts are guaranteed debt, which are debts that have guarantees provided by Hengda Real Estate, its subsidiary companies, or third parties, according to their latest financial results. The remainder consists of unsecured borrowings (RMB
10.9bn), onshore bonds (RMB 50.9bn) and offshore bonds (RMB 33.6bn). The company has also provided guarantees, possibly to non-consolidated subsidiary companies and to suppliers, which was RMB 31.8bn at the end of Jun 2021
Ultimately, the recovery prospects remain unclear. In aggregate, with leverage at Hengda Real Estate likely higher than the reported book leverage due to large amounts of payables, the uncertainties regarding the strength of the keepwell structure, and sizeable amounts of secured indebtedness, it is difficult to ascertain the recovery prospects for the TIANHL bonds. As with the EVERRE bonds, there are considerable amounts of uncertainties, though according to Goldman, it is "worth noting that the TIANHL bonds do benefit from guarantees from a number of offshore subsidiary companies, and they may provide some additional value." We disagree and are confident that when the house of cards comes tumbling down, it will become clear just how worthless creditor "guarantees" in China truly are.
But while investors in Evergrande bonds will inevitably suffer the consequences of their own stupidity - sorry guys, it was obvious to all what was coming and if you held on until now, you have only yourself to blame - the bigger question is how big of a shockwave will the rest of the world, i.e., those people who did not volunteer to buy Evergrande bonds or stock, suffer. This brings us to the...
Conclusion: What should investors be watching for.
The primary thing investors should be watching out for in the coming weeks/ months will be upcoming coupon payments on offshore bonds, as this could be the trigger for a credit event. As note above, coupon payments on offshore bonds are due on the 23/09, 29/09 and 11/10 .
The second thing to watch will be the price action in other high beta B-rated developer credits, something which UBS thinks will provide a useful gauge of systemic risk in the property sector as well as consensus expectations with respect to what an Evergrande credit event might look like. Curiously, spill over into other high beta B-rated developer credits has been fairly muted thus far, with investors perhaps still hopeful of a creditor friendly resolution for Evergrande and fundamentals generally having sequentially improved through H1 21' despite increased regulation/tighter Chinese credit which will crush fundamentals in the second half.
The third and final thing to watch will be Chinese credit/property policy, or what Beijing will do. While consensus is that the government is set to stay tight generally on property policies but not to escalate tightening further, local governments may ease the implementation if housing construction decline sharply for a few months, something which should help provide some sentiment relief for issuers across the sector.
As for Beijing, should the contagion - whether domestic or international - become unbearable in terms of economic, markets or social strain, China will have no choice but to sweep aside its futile hopes of constraining debt expansion - after all, according to the IIF, China's debt/GDP is already well above 350%, a level where if it doesn't keep growing exponentially it assures a collapse.
As such, while covid was the trigger greenlighting trillions in fiscal and monetary stimulus to jump-start the voluntary rebooting of the world after the covid lockdowns, the Evergrande collapse and resulting crisis could be the event that offers a "begrudging" Beijing the justification to launch the next mega stimulus, one which will result in a reflationary tidal wave, send cryptos soaring higher, and force the rest of the developed world to follow suit with tens of trillions of stimulus of their own as the race to the fiat bottom enters its final lap. Because, whether in China or the US, whether communist or crony capitalist, a politician always know never to let a crisis go to waste.
362,41641